Diuretics:
A diuretic is a substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This can be a drug, or any other substance. Diuretics are often referred to as “water pills” and are used to increase the amount of water and salt excrete out from the body as urine.
They are commonly used to treat conditions like high blood pressure and congestive heart failure.
CLASSIFICATION in TERMS of Site of Action:
- Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitor: (Post convoluted tubule)--- Acetazolamide
- Osmotic Diuretics: (Descending limb of Henlie's Loop)--- Mannitol
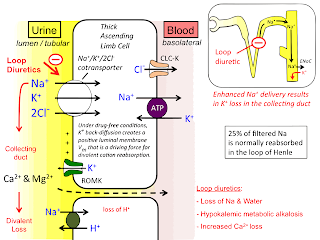
- Loop Diuretics (Na+-K+-2Cl- Symporter inhibitors)/ High ceiling: (Ascending Limb of Loop of Henle) --- Furosemide
- Inhibitors of Na+ Cl- symport (Thiazide and thiazide-like Diuretics): (DCT) ---Chlorothiazide
- K+ Sparing Diuretics (Inhibitors of renal epithelial Na+ channels): (Collecting Tubule)--- Spironolactone
How do loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics differ in their mechanisms of action at the molecular level?
|
|
Loop Diuretic |
Thiazide Diuretic |
K+ sparing Diuretic |
|
Site of Action |
Ascending Limb of Loop of Henlie |
Distal Convoluted Tubule |
Collecting Duct |
|
Specific Binding |
Na+K+2Cl-
Cotransporter |
Na+Cl-
Symporter |
Renal Epithelial Na+
channel & Na/ K ATPase pump |
|
MOA |
Blocks
the Na+K+2Cl- Cotransporter (Competitive inhibition of Cl- binding site) ¯ Inhibits
Na, Cl and K reabsorption ¯ Urine ¯ ¯ Blood volume |
Blocks
the Na+Cl- Symporter ¯ ¯ Reabsorption of Na, Cl ¯ Excretion of Na, Cl ¯ Urine |
Aldosterone
Receptor Blocker ¯ ¯ Expression of Lumen Na channel → ¯ Transport of Na to the Collecting
tubule cell & ¯ Expression Na/ K ATPase pump → ¯ Transport of Na to Blood (¯ K to the urine) ¯ Na and Water in the urine
|
|
|
|
|
|
Side effects
- Hypokalemic Metabolic Alkalosis
- Risk of Acidosis (K+ sparing)
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Dehydration
- Diarrhea
- Muscle Weakness (Decreased Calcium)
- Renal Stone (chronic use)
- Hyperuricemia



.png)

Comments
Post a Comment