Cardiac Glycoside
DEF- Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump.General structure-
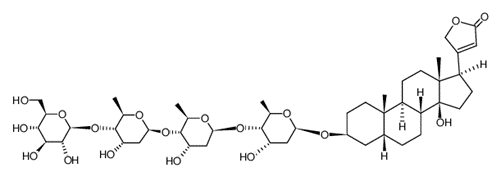
ð All glycosides consists of an aglycone which is attached to one or more sugar (glycone) moieties.
ð The Aglycone part have the pharmacological activity → Attached sugar moiety modify the solubility and Permeability.
ð The Aglycone part consist of Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene (Steroid) ring to which a 5 (Cardenolide) or 6 (Bufadienolide) membered unsaturated lactone ring is attached.
ð
One
or more -OH or other substituents are present to the aglycone to determine its
Polarity.
Example - Digitalis
|
DIGITALIS |
|||
|
Biological
Source |
Plant
Part – Dried leaves Scientific
Name – Digitalis pupurea Family
– Scrophulariaceae |
||
|
Morphology
|
Odour:
odourless Taste:
Distinctly bitter Length:
10 – 30 cm, Width: 4 – 10 cm Shape:
Ovate, Lanceolate, petiolate |
||
|
Chemical
Constituents |
Primary glycoside: -
Purpurea glycoside A and
B Secondary
Glycoside: -
Digitoxin, Digoxin Primary
glycosides are less significant than Secondary glycosides |
||
|
Uses
|
1. Used
in treatment of Congestive Heart failure 2. Preparation
of Digoxin 3. Treatment
of articular fibrillation |
||



.png)

Comments
Post a Comment